Credit: Alison Yin / EdSource
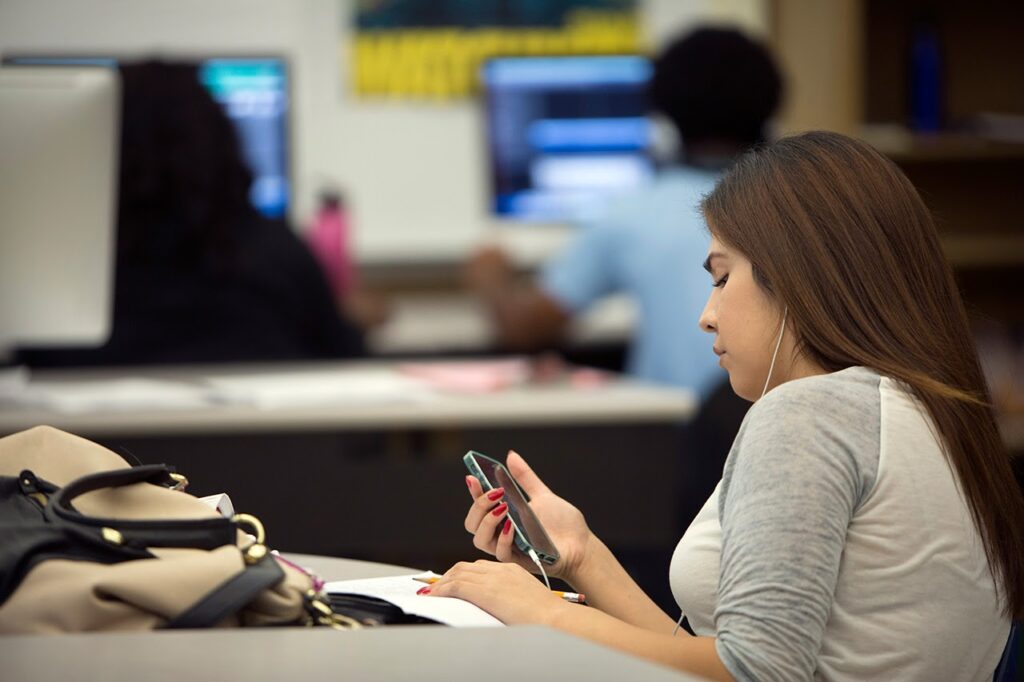
In California and across the United States this year, policies banning or restricting student cell phone use on school campuses are being enacted in an effort to curb bullying, classroom distractions, and to combat addiction to the devices.
“It’s part of the zeitgeist right now, and there is a trend toward cell phone restriction,” said Troy Flint, spokesman for the California School Boards Association. “There’s more scrutiny of the issue now than there was previously.”
Lincoln Unified School District in Stockton, Santa Barbara Unified, San Francisco Unified, and Roseville City School District and Folsom Cordova Unified near Sacramento are among the California districts starting the school year with cell phone restrictions on their campuses.
Cell phone restrictions look different across the state, depending on school district, school or even individual teacher’s policies. In some schools, students entering a campus or classroom are required to put their phones in an electronic pouch that can only be unlocked by school staff with a special magnet. In other schools, cell phones are turned off and put in lockers in the classroom. More commonly, students are asked to turn off their phones and to put them in their backpacks or pockets during class time.
California district leaders got a nudge from Gov. Gavin Newsom last week when he urged them to take immediate steps to restrict cell phone use this academic year. Newsom reminded school leaders that legislation signed in 2019 gives them the authority to regulate smartphones during school hours.
“Excessive smartphone use among young people is linked to increased anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues,” Newsom said in a letter to school leaders on Aug. 14.
California lawmakers are also considering proposed legislation to restrict student cell phone use on all public school campuses, a mandate at least five other states have already enacted. Without a statewide mandate, it’s up to districts, schools, or teachers to implement a policy.
San Diego Unified officials have indicated they are studying the issue, while Los Angeles Unified, the state’s largest school district, is finalizing a policy that will ban student cellphone and social media use. It will go into effect in January.
“Kids no longer have the opportunity to just be kids,” said Nick Melvoin, the LAUSD school board member who authored a resolution calling for the policy. “I’m hoping this resolution will help students not only focus in class, but also give them a chance to interact and engage more with each other — and just be kids.”
Melvoin commended Newsom for encouraging other districts to follow suit.
“I have seen the positive effects firsthand at schools that have already implemented a phone-free school policy, and look forward to seeing the benefits of this policy take hold district wide next semester,” Melvoin said.
But the policies have had pushback from some parents who fear losing touch with their children during emergencies.
“Some parents, some families feel that the cell phone is essential for notification in the case of a natural disaster, a school emergency, or a school shooting,” said the CSBA’s Flint. “Or some people use it for less extreme, but still important reasons, like monitoring their kids’ required medicine. Some families with students with disabilities like to have an additional level of contact with their students at schools.”
Cell phone addiction is a problem
School cell phone bans gained momentum nationally in May when Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory calling on policymakers, technology companies, researchers and families to minimize the harm of social media and to create safer, healthier online environments to protect children online.
Murthy said there is growing evidence that social media use is associated with harm to a young person’s mental health, adding that 95% of children between the ages of 13 and 17 use at least one social media platform, and more than a third use social media constantly.
Santa Barbara Unified has made mental health a priority when it comes to cell phone use on campus. The Off and Away policy requires cell phones be turned off and put away in classrooms, and anywhere on a campus where learning is taking place, said Assistant Superintendent ShaKenya Edison.
Punishment for not complying with the policy ranges from students and parents being required to meet with school staff, to confiscating phones. Students may be referred to counseling or a therapist if necessary, Edison said.
“One of the things that the (planning) committee was very clear about – we had doctors also on our committee and psychologists – is that we need to treat cell phone usage as an addiction, not as defiance,” Edison said. “So it really is trying to get at the root of the dependency of the phone.”
Students became more reliant on cell phones and smartwatches during the Covid pandemic when the devices were the only way they could connect to their social circle, Edison said. Students sometimes use their phone to deal with the anxiety of being in the classroom, or when they are struggling with academics, she said.
University of San Francisco researchers found that 12- to 13-year-old children in the U.S. doubled their non-school related screen time from 3.8 hours a day to 7.7 hours a day when campuses were closed during the pandemic.
Warning signs of smartphone addiction in students include becoming distressed at the thought of being without their phone, thinking about their phone when not using it, interrupting whatever they are doing when contacted on their phone, or having arguments with others because of phone use, said Jason Nagata, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco.
Santa Barbara Unified is taking on the cell phone addiction problem inside and outside the classroom. Along with including parents in the planning of the program, the district offers parents information about monitoring social media and age-appropriate apps on their website.
“We receive gratitude from parents saying, ‘Thank you for tackling this. I’m trying to tackle it at home, and I don’t know how to tackle the dependency. So thank you for at least dealing with it on the school site,’ ” Edison said.
Students are more focused without phones
Andrea Blair-Simon says the ban on cell phone use in the Folsom Cordova Unified School District, allows her eighth-grade daughter, Laila, to fully focus on her studies in the classroom and to socialize with others during breaks and lunch. She had previously watched her daughter sit with her friends texting one another instead of talking.
“I love the cell phone policy,” Blair-Simon said. “I think it benefits the kids. I think it benefits the teachers. I’m not saying don’t have it (a cell phone), I’m just saying it’s not necessary during school hours. Before or after, do whatever you want. It’s your life. It’s your own time. But when you’re on a teacher’s time – school time – using school resources, listen to your teacher.”
The no-phone policies also curtail online bullying, Blair-Simon said. Things like posting unflattering pictures with mean comments can adversely impact young people who have hyper-social awareness about themselves, she said.
In its cell phone policy updated last year, Folsom Cordova Unified no longer permits students in transitional kindergarten through eighth grade to use cell phones, smartwatches or other mobile communication devices, anywhere on campuses during the school day. High school students can’t use them in classrooms.
Last year Laila and her classmates were required to use a lockable Yondr Pouch, which allows students to keep their phone, but with no access to it unless a teacher or school administrator unlocks the pouch. Now, instead of pouches, students have been asked to turn off their phones and put them away.
“This year there are no warnings, and you are to be sent straight to the office,” Laila said. “This year they have a little locker in the office, like a phone locker, and it has to be locked in there until the end of the day, if they catch you with it.”
Laila would like to have her phone at lunch or during passing periods, but acknowledges that students are more focused and are spending more time talking to one another during breaks than before the ban.
Policies improve school climate
Drama teacher Keith Carames says there has been a positive shift in culture and climate at James Lick Middle School in San Francisco since the school began requiring students to lock their phones in a Yondr Pouch at the beginning of the school day.
“There’s been a significant shift away from the buzzing and the distractions,” Carames said. “There’s been a significant decrease in digital bullying.”
The school is part of San Francisco Unified, which requires cell phones, smartwatches and other mobile devices to be turned off and put away during classes and passing periods.
James Lick Middle School has its own, stricter policy which requires students to present a lockable pouch, provided by the school, when they show up on the campus – empty or not. If the student does not have their pouch, the phone is confiscated. If a student’s phone is not in the pouch during the school day, security is called to confiscate it, Carames said.
Some school districts in the state without district-wide cell phone bans allow individual schools to make their own rules about cell phone use on their campus.
Fresno Unified relies on a 20-year-old policy that prohibits students from using phones in an inappropriate and disruptive way, like invading someone’s privacy, cheating on tests or ridiculing or shaming someone. Students who violate the policy can have their phones confiscated, or can be suspended or expelled.
The board policy is the “minimum requirement” for the district, Fresno Unified spokesperson AJ Kato told EdSource Wednesday. Each school determines how the policy is implemented on its campus and has the discretion to go beyond what the policy dictates.
Bullard High in Fresno Unified introduced the Yondr Pouch in 2022 to create a phone-free campus, The Fresno Bee reported. Students must lock their phones in the pouch during the school day – even during lunch. After 2022-23, the first school year with the pouches, Bullard High officials credited its 17% improvement in English proficiency to the restriction, The Bee reported.
Teachers largely support restrictions
Teachers nationwide say that cell phones are a major distraction for students in class, according to Pew Research released in 2023. A third of public K-12 teachers surveyed for the report said that cell phones are a major problem in their classrooms, while 20% said they are a minor problem. Almost three-quarters of the high school teachers surveyed said phones are a major distraction to their students, compared to 33% of middle school and 6% of elementary school teachers.
Cell phone disruptions in the classroom have been a recurring topic for teachers and administrators at staff meetings in the Roseville City School District, said school board member Jonathan Zachreson.
Some teachers in the district conducted an informal experiment, asking students to note how many times they received alerts on their phones during class. The teachers discovered that the students who had the most alerts were performing worse than others academically, Zachreson said.
The K-8 district near Sacramento put a new cell phone policy in place this year to cut down on classroom distractions and behavior problems. The policy requires students to turn off cell phones, personal tablets, Bluetooth headphones or smartwatches and to store them away during school hours.
The district’s elementary schools already had a no-phone policy, but it was not enforced uniformly across the district, Zachreson said. The district decided to put a uniform policy in place and to expand it to all grade levels.
Even without district policies, some teachers have banned cell phones in their classrooms. Nicolle Fefferman, a longtime LAUSD educator and co-founder of the Facebook group Parents Supporting Teachers, is one of them. When cellphones are not tucked away, Fefferman said it can be challenging for teachers to “police” cell phone use.
“I would tell my students: ‘I see you for so little time every day that I’m really selfish. I’m really greedy,’” Fefferman said. “‘I want every minute of your attention for the work that we’re doing together in this class.’”

United Teachers Los Angeles, the union representing more than 35,000 educators across LAUSD, supports the board’s decision to implement a district-wide policy.
“For these policies to be effective, strong collaboration is essential,” Gina Gray, an LAUSD middle school English teacher, told EdSource in a statement on behalf of the union.
“School district administrators must work closely with educators and parents to implement these changes,” Gray said. “Educators care deeply about the well-being of our students, and their families should be included in decisions about changes to our school communities.”
California Teachers Association President David Goldberg agrees: “Our union has supported improving school environments and restricting the use of smartphones on campuses,” he said in a statement. “As educators, we always seek to help our students reach their full potential, and we are moved by the data, listening to our students and their families, and our own experiences showing that smartphones can be a distraction and harmful to the mental health of students.”
Cell phone bans gain national momentum
California may soon join Florida, Indiana, Louisiana, Indiana and Ohio in passing legislation that bans or restricts cell phone use on public school campuses.
Although California law allows districts to restrict the use of cellphones on campus, it does not require them to. That could change if a bill working its way through the Legislature passes. Assembly Bill 3216 would require school districts to adopt a policy to limit or prohibit the use of smartphones by students. The bill passed the Senate Appropriations Committee last week and is likely to make it to the governor’s desk for final approval, according to School Services, an education consulting company.
Another piece of legislation, Senate Bill 1283 would allow, but not require, districts to limit students’ use of social media while on campus. The bill is expected to get a vote on the Assembly floor this month.
The bills have bipartisan support.
“Josh Hoover’s a Republican who’s putting forth this legislation (Assembly Bill 3216),” Zachreson said. “Gavin Newsom is pushing school districts to take action. You have Ron DeSantis and an Arkansas governor doing the same thing. I mean, when you have Gavin Newsom and Ron DeSantis on the same page, I think you have a winning issue.”